The recent surge in Artificial Intelligence has changed how people view its potential uses. Nevertheless, AI has always been a part of our daily lives, even in cars, albeit in a more behind-the-scenes capacity.
Since the first gasoline engine vehicle was created by Karl Benz, the co-founder of Mercedes Benz, in 1886, a higher level of vehicle automation has been continuously implemented into cars, requiring AI’s involvement.
Let’s explore the history of self driving vehicles to understand how AI has become crucial to improve safety standards. First, we have a look at the different levels of vehicle automation and the level of human interaction required.
The different levels of vehicle automation:
- Level 0: No automation
- Level 1: Driver assistance. The car has a single automated system, i.e. cruise control.
- Level 2: Partial Automation. The vehicle can autonomously assist the driver with steering and acceleration maneuvers.
- Level 3: Conditional Automation. The vehicle has environmental detection capabilities and can adapt to such with little human control. This includes reacting to changing road conditions, pedestrians, and sudden lane changes.
- Level 4: High Automation. The vehicle can perform all driving tasks under specific circumstances, but geofencing is required and human interaction may be required.
- Level 5: Full automation. The vehicle performs all driving tasks under all conditions. No human attention is required.
The history of self driving cars
AI presence in vehicles began in 1987 when Ernst Dickmanns launched its fully automated car, the first of its kind. This car was capable of self driving without human assistance in traffic-free environments.
In the past, machines were unable to imitate human abilities, but now they could. This led to the development of advanced driving systems that can make decisions without human input. Any issue caused by these technological advancements could also be solved through machine learning.
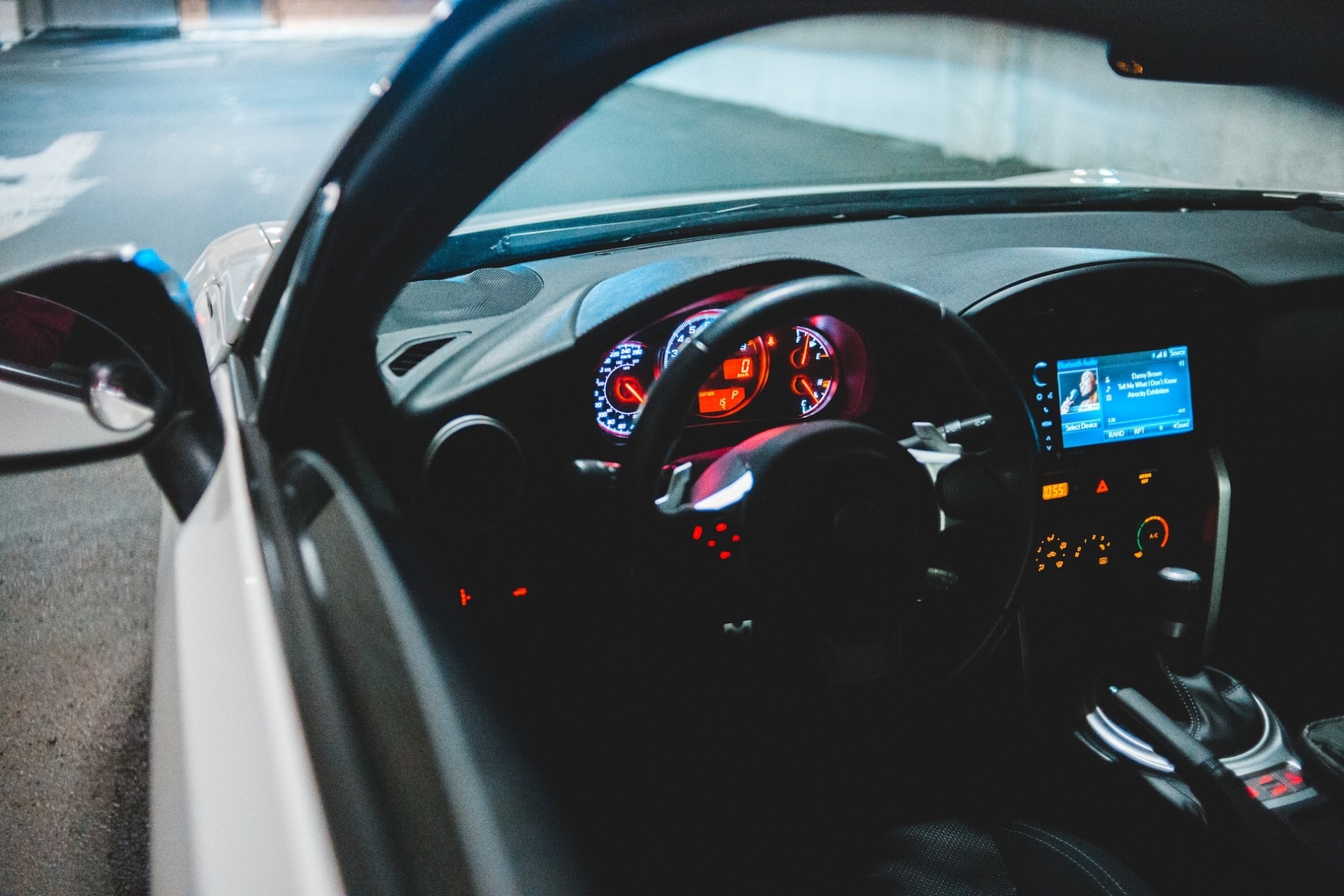

Windows released its speech recognition software in 1997. The same technology is now used in Google Maps. Speech recognition significantly improves driving safety by reducing distractions from looking down at a screen to navigate maps or respond to calls. It is a prime example of modern technology that can eliminate the dangers caused by obsolete technology.
RELATED ARTICLES: 5 Small EVs for Sustainable Cities | World’s Electric Vehicle Fleet Will Soon Surpass 20 Million | Long-Range Electric Vehicles for Under $40k | Is Using Synthetic Fuels A Sustainable Alternative To Buying Electric Cars? | How Electric Cars Became Cool | London Electric Cars, Converting Classic Cars into Modern EVs |
In 1998, Toyota brought Adaptive Cruise Control (ACC) to the car industry. This allowed the car to keep a set distance from other vehicles while maintaining a certain speed. ACC laid the foundation for Level 3 robotic cars. These include the temporary autopilot feature by Volkswagen in 2012 and Tesla Lane Control in 2014.
The driverless cars era was just beginning.
How self driving Cars Work
A self driving car operates without the need for human drivers. Current autonomous vehicles are Level 3 cars. This level of automation means they can perform most driving tasks themselves, but human intervention and authorization are still required.
Essentially, these robotic cars learn just like humans, but their “brains” are pre-programmed with algorithms trained by expert drivers, giving them advanced decision-making capabilities. AI-structured vehicles monitor their environment, such as the car’s position, traffic lights, human motion, and public roads. This information is processed with high-powered machine learning to output results through the car speed, brakes, lights, and every factor it mechanically controls.
Learning by experience
For example, if a pedestrian is ahead of the car, the AI will observe this through camera sensors and engage the brakes so the car can slow down to avoid an accident. Machine learning is a necessary component for adapting to constantly new environments regarding people, cars, and roads. Those might be different from the existing ones embedded in the car systems. Ultimately, the more environments the car experiences, the more data it collects as a part of its learning process.
Advanced driver assistance systems allow human error to be kept at a minimum since decisions are made much more quickly without emotional distractions. Specifically, this could help in life-saving scenarios where the driver loses the capability to control the vehicle. The system could also be further developed through machine learning so that it can adapt to each person driving style and recognise dangerous habits to avoid.
Driver assistance technologies in the automobile industry bring more safety, could solve many other issues brought by technology, and improve vehicle lifespan. These newer safety features are crucial in a world where data are the key to overcoming everyday driving challenges.
Present-day cars now aim to include many Level 4 features, an example being the interior cameras in Tesla cars, which monitor drowsiness via the driver’s eyes and significantly avoid the risk of collisions. Tesla is leading the charge regarding autonomous driving, producing one of the world’s first self driving cars to be used globally.
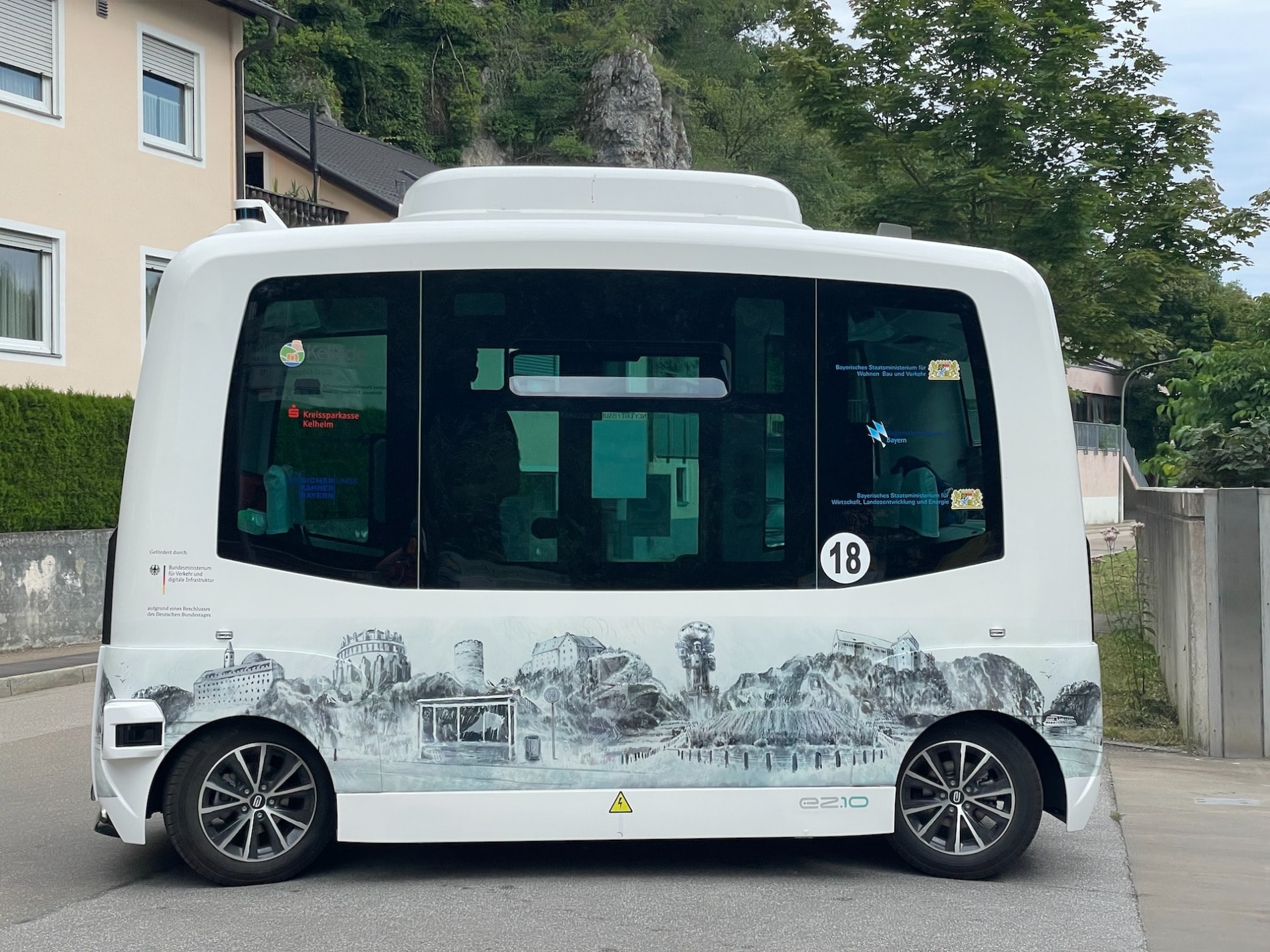

The potential dangers of level 5 cars
The growth potential of this technology lies more in its safety features rather than its high-performance capabilities. Moreover, it creates more inclusivity for individuals who have difficulty driving, such as older adults or those with mobility impairments.
However, despite all these benefits, risks will always be present. Since last year, issues with Tesla autopilot caused dozens of deaths. Furthermore, if self driving cars prove to be as successful, many cars will be connected through GPS systems and tracking, but this greatly increases the risk of hacking. Sensors and cameras used for your safety can quickly become avenues for security breaches and personal data leaks.
This opens the question of whether Level 4 and up cars are even viable in our society. It will be a matter of how much tracking and information would we be willing to share in the pursuit of safety and comfort.
For instance, Google’s waymo project offers autonomous car rides similar to Uber, providing safety technologies by using various camera sensors to observe roads like human drivers. The questions of data risks arise when these multiple sensors may lose effectiveness, suffer damages, or are manipulated due to the cloud connection surrounding the driverless cars.
If a potential cyber threat was to occur, user personal data could be breached, so strict regulations need to be created to protect users. If these vehicles are also open to public use, quality control measures must be established to ensure no damages or faults occur between rides.
Can you buy self driving cars? Are they the right choice for you?
Autonomous vehicles were initially developed to overcome the constraints of the automotive industry. Today, they could become an agent of positive change in driving experiences globally.
Presently, self driving cars such as the Tesla Model S and Model X are legal to drive in most countries, so their availability is no longer an issue. So now that they’re in the market, should you buy one?
Firstly, looking at the main feature of buying any vehicle, the cost of the partially automated vehicles in the current market is similar to their Level 0 counterparts. However, most models are much pricier than your average compact car. In the future, fully autonomous vehicles could be over $200,000 more expensive than their Level 3 counterparts.
Inclusivity may be an issue due to this massive barrier in purchasing. Still, once more companies break into the market and competition increases, these new vehicles should be far more affordable.
To what extent do the unique features of self-driving cars bring benefits? According to the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) their primary advantage is safety. Autonomous vehicles can eliminate human errors such as distractions, fatigue and potentially avoid drunk driving, preventing numerous crashes.
Sales of Autonomous Cars (in million units)
| Year | Sales (in M) |
|---|---|
| 2019* | 1.4 |
| 2020** | 1.96 |
| 2021** | 2.76 |
| 2022** | 3.87 |
| 2023** | 5.42 |
| 2024** | 7.61 |
| 2025** | 10.67 |
| 2026** | 14.97 |
| 2027** | 21.01 |
| 2028** | 29.47 |
| 2029** | 41.34 |
| 2030** | 53.86 |
A future full of autonomous vehicles?
The idea that autonomous vehicles lead to more efficient driving, an easier lifestyle, and higher labour productivity is often used to justify infrastructure and technology investment. The reality is, autonomous drive and vehicle electrification go hand in hand with modern economies’ vision for the future, where harmful emissions could be significantly lowered.
Furthermore, there might be unknown issues in the future that new vehicle technologies could address. Think back to the COVID pandemic, which posed problems that weren’t even in our realms of consideration in 2019. Autonomous cars would have allowed vulnerable people in isolation to travel alone in self driving cars without the risk of getting ill.
Self-driving cars are becoming increasingly popular and are being developed at an exponential rate. Although they may not currently be a viable option for everyone, their benefits for safety, personal use, and comfort are already there and will continue to improve as technology evolves and costs decrease.
It’s possible that seeing a car without a driver may become the new norm in the future.
Editor’s Note: The opinions expressed here by the authors are their own, not those of Impakter.com. — In the Featured Photo: A self driving Tesla. Featured Photo Credit: Unsplash.