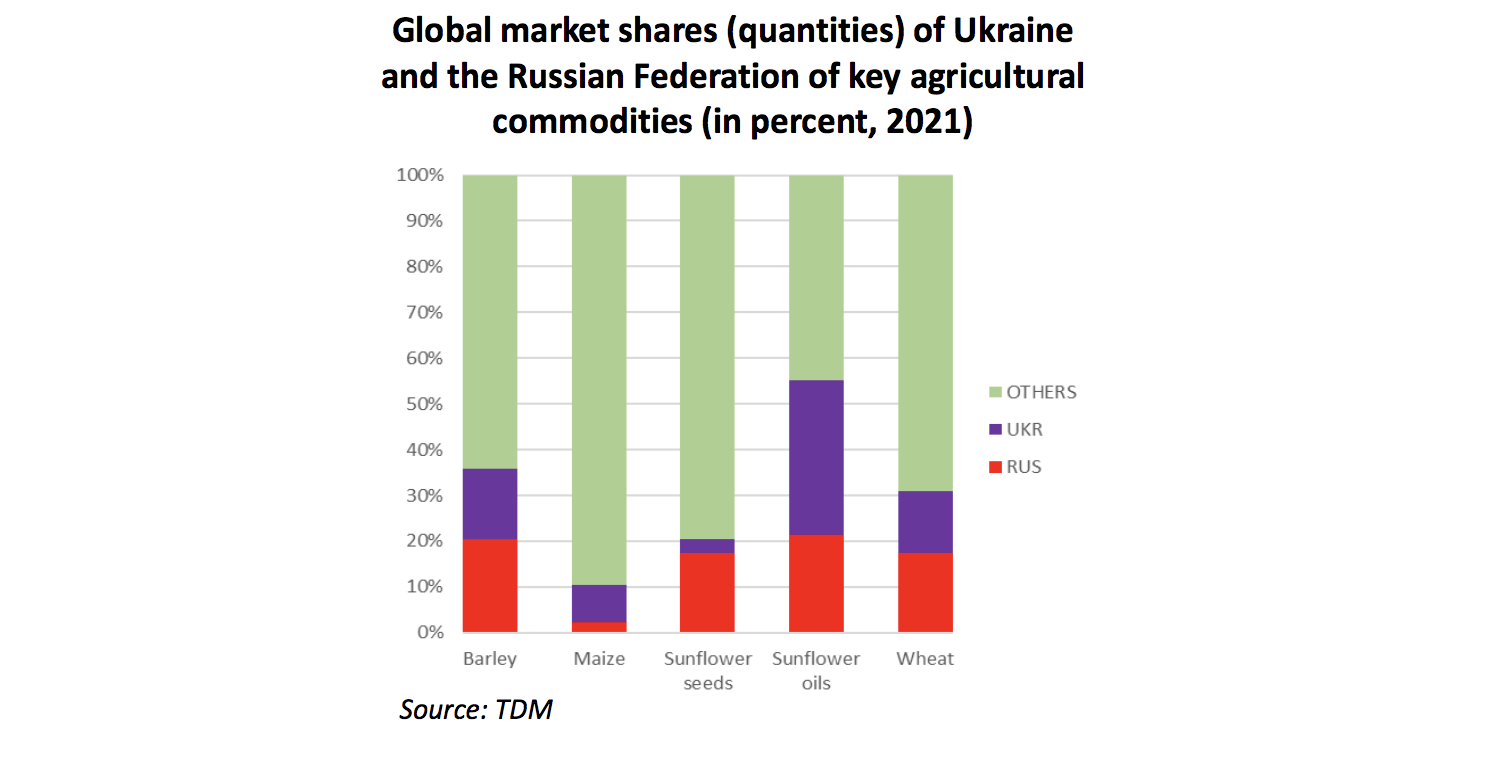
Over the past two years, COVID-19 has presented many challenges to global food security. Today, what is happening in Russia and Ukraine adds another significant challenge. Russia and Ukraine play a substantial role in the global food production and supply. Russia is the world’s largest exporter of wheat, and Ukraine is the fifth largest. Together, they provide 19% of the world’s barley supply, 14% of wheat, and 4% of maize, making up more than one-third of global cereal exports. They are also lead suppliers of rapeseed and account for 52% of the world’s sunflower oil export market. The global fertilizer supply is also highly concentrated, with Russia as the lead producer.
Over the past two years, COVID-19 has presented many challenges to global food security. Today, what is happening in Russia and Ukraine adds another significant challenge. Russia and Ukraine play a substantial role in the global food production and supply. Russia is the world’s largest exporter of wheat, and Ukraine is the fifth largest. Together, they provide 19% of the world’s barley supply, 14% of wheat, and 4% of maize, making up more than one-third of global cereal exports. They are also lead suppliers of rapeseed and account for 52% of the world’s sunflower oil export market. The global fertilizer supply is also highly concentrated, with Russia as the lead producer.
Supply chain and logistical disruptions on Ukrainian and Russian grain and oilseed production and restrictions on Russia’s exports will have significant food security repercussions. This is especially true for some fifty countries that depend on Russia and Ukraine for 30% or more of their wheat supply. Many of them are least developed countries or low-income, food-deficit countries in Northern Africa, Asia and the Near East. Many European and Central Asian countries rely on Russia for over 50% of their fertilizer supply, and shortages there could extend to next year.
27 percent of global exports of wheat are from Russia or Ukraine. For countries in the Global South, it's even higher: 100 percent of Somalia's wheat imports come from Russia or Ukraine. What is unfolding now will be a terrible disaster for the global poor.
— Gravel Institute (@GravelInstitute) March 18, 2022
Food prices, already on the rise since the second half of 2020, reached an all-time high in February 2022 due to high demand, input and transportation costs, and port disruptions. Global prices of wheat and barley, for example, rose 31% over the course of 2021. Rapeseed oil and sunflower oil prices rose more than 60%. High demand and volatile natural gas prices have also driven up fertilizer costs. For instance, the price of urea, a key nitrogen fertilizer, has increased more than threefold in the past 12 months.
The war in #Ukraine is already impacting millions of lives inside AND outside the country.
Food prices reached a new all-time high in February according to the @FAO Food Price Index.
The collateral damage? Catastrophic global hunger 👇🎦 pic.twitter.com/QT17H4jiNF
— WFP Africa (@WFP_Africa) March 14, 2022
The conflict’s intensity and duration remain uncertain. The likely disruptions to agricultural activities of these two major exporters of staple commodities could seriously escalate food insecurity globally, when international food and input prices are already high and volatile. The conflict could also constrain agricultural production and purchasing power in Ukraine, leading to increased food insecurity locally.
Core Risk Factors Identified
Cereal crops will be ready for harvest in June. Whether farmers in Ukraine would be able to harvest them and deliver to the market is unclear. Massive population displacement has reduced the number of agricultural laborers and workers. Accessing agricultural fields would be difficult. Rearing livestock and poultry and producing fruits and vegetables would be constrained as well.
The Ukrainian ports on the Black Sea have shuttered. Even if inland transportation infrastructure remains intact, shipping grain by rail would be impossible because of a lack of an operational railway system. Vessels can still transit through the Turkish Straits, a critical trade juncture through which a large amount of wheat and maize shipments pass. Rising insurance premiums for the Black Sea region would exacerbate the already high costs of shipping, compounding the costs of food imports. And, whether storage and processing facilities would remain intact and staffed is also still unclear.
Related Articles: Ukraine War: How It Impacts Food | Assembling the Puzzle: Conceptual Framework and Methods for Assessing Food Systems
The Russian ports on the Black Sea are open for now, and no major disruption to agricultural production is expected in the short term. However, the financial sanctions against Russia have caused an important depreciation which, if continued, could undermine productivity and growth and ultimately further elevate agricultural production costs.
Russia is a major player in the global energy market, accounting for 18% of global coal exports, 11% of oil, and 10% of gas. Agriculture requires energy through fuel, gas, electricity use, as well as fertilizers, pesticides, and lubricants. Manufacturing feed ingredients and feedstuffs also require energy. The current conflict has caused energy prices to surge, with negative consequences on the agriculture sector.
Wheat is a staple food for over 35% of the world’s population, and the current conflict could result in a sudden and steep reduction in wheat exports from both Russia and Ukraine. It is still unclear whether other exporters would be able to fill this gap. Wheat inventories are already running low in Canada, and exports from the United States, Argentina and other countries are likely to be limited as government will try to ensure domestic supply.
Wheat: top exporters and importers#AFPgraphics map showing the top 10 wheat importing and exporting countries, in millions of tonnes, in 2020, according to the United Nations Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) pic.twitter.com/z9OjuPg6Km
— AFP News Agency (@AFP) March 15, 2022
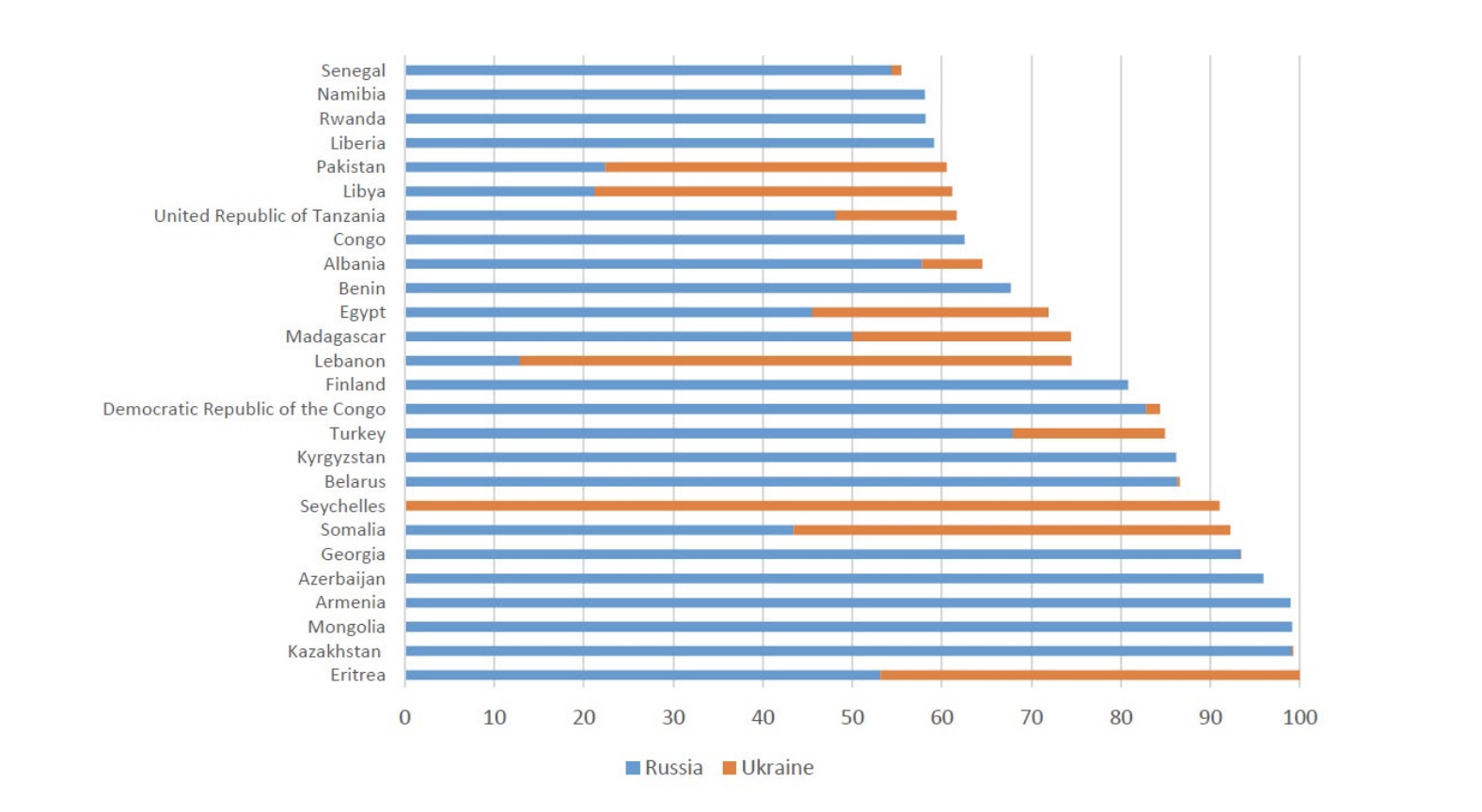
Countries reliant on wheat imports are likely to ramp up levels, adding further pressure on global supplies. Egypt, Turkey, Bangladesh, and Iran are the top global wheat importers, buying more than 60% of their wheat from Russia and Ukraine, and all of them have outstanding imports. Lebanon, Tunisia, Yemen, Libya, and Pakistan also rely heavily on the two countries for their wheat supply. Global maize trade is likely to shrink due to expectations that the export loss from Ukraine will not be filled by other exporters and because of high prices.
Wheat Import Dependency (percent, 2021)
Export prospects for sunflower oil and other alternative oils also remain uncertain. Major sunflower oil importers, including India, the European Union, China, Iran, and Turkey, must find other suppliers or other vegetable oils, which could have a spill-over effect on palm, soy, and rapeseed oils, for example.
Policy Recommendations
- Keep global food and fertilizer trade open. Every effort should be made to protect the production and marketing activities needed to meet domestic and global demands. Supply chains should keep moving, which means protecting standing crops, livestock, food processing infrastructure, and all logistical systems.
- Find new and more diverse food suppliers. Countries dependent on food imports from Russia and Ukraine should look for alternative suppliers to absorb the shock. They should also rely on existing food stocks and diversify their domestic production to ensure people’s access to healthy diets.
- Support vulnerable groups, including internally displaced people. Governments must expand social safety nets to protect vulnerable people. In Ukraine, international organizations must step in to help reach people in need. Across the globe, many more people would be pushed into poverty and hunger because of the conflict, and we must provide timely and well-targeted social protection programs to them.
- Avoid ad hoc policy reactions. Before enacting any measures to secure food supply, governments must consider their potential effects on international markets. Reductions in import tariffs or the use of export restrictions could help to resolve individual country food security challenges in the short term, but they would drive up prices on global markets.
- Strengthen market transparency and dialogue. More transparency and information on global market conditions can help governments and investors make informed decisions when agricultural commodity markets are volatile. Initiatives like the G-20’s Agricultural Market Information System (AMIS) increases such transparency by providing objective and timely market assessments.
Editor’s Note: The opinions expressed here by Impakter.com columnists are their own, not those of Impakter.com. — In the Featured Photo: Wheat fields in Ukraine. Featured Photo Credit: Wikimedia Commons.