The Coronavirus — Where It Stands
This past Sunday, February 23rd, there were a total of 79,205 reported cases of the coronavirus. In deaths, there were 2,470 reported cases. Considering the 23,419 reported recoveries from the virus, the statistics for the virus appear to be pointing toward a positive outcome. As of February 25th, the total number of reported cases rose to 80,427 while the number of recoveries rose to nearly 28k.
With these statistics in mind, the number of total cases is rising at a rate of less than 1% per day. Meanwhile, the number of recoveries is rising at roughly 8% per day. Additionally, all cases with outcomes are now at a recovery rate of 91%. Compared to the rate of roughly 60% three weeks ago, it seems almost confirmed that we can soon rest easy without any fear of the coronavirus.
Effects on Economies
The impact of the virus extends farther than that of the individuals (and their families) affected, however. European economies and, more specifically, businesses reliant on tourism activity have recently seen a dip in their revenue due to travel bans implemented for health security. Roughly 70 airlines worldwide have canceled international flights to and from China, causing European (and other) economies to lose some of their wealthiest regular tourists.
Many citizens from countries not restricted under travel bans have chosen to avoid travel altogether, leading to an even greater deficit in tourism business’ revenue. The International Civil Aviation Organization predicts that Japan may see a deficit of 1.29 billion USD in lost tourist revenue while Thailand misses out on 1.15 billion USD from the lack of Chinese travelers.
Tourist revenues dived in Italy, the new epicenter of the virus in Europe. Confturismo expects that there will be 22 million fewer tourists in Italy over the next three months. But all sectors are affected. Prometeia, an Italian economic research agency, estimates that GDP will contract by 0,3% because of the virus. Confcommercio, the Italian retail business association, expects losses to range between 5 and 7 billion euros should the outbreak last until May.
Related Articles: Coronavirus Political Risks | Coronavirus and Animal Policies
Europe, Thailand, and Japan are hardly the only economies affected by these economic ramifications.
China, in many ways, the manufacturing hub of the world with global supply chains, is deeply hit. Chinese economic growth is expected to slow to 4.5%, a nearly record low. Aside from the obvious blow to China’s economy, the ripple effects are felt in both Europe and America.
American companies are now feeling the economic effects of the coronavirus. With their product parts primarily being manufactured in China, large American corporations such as Apple, Nissan and Hyundai are seeing their partner factories either slowing in production or shutting down entirely.
American travel agencies are expected to see reductions in revenue as well, part of an estimated reduction of 4-5 billion USD worldwide.
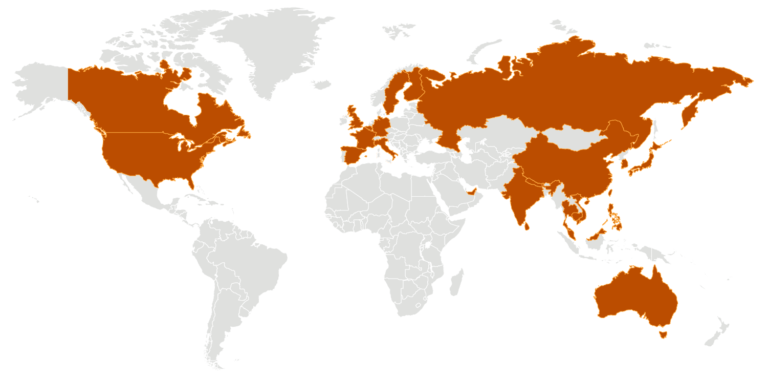
In response to the spreading virus, the annual National People’s Congress meeting was postponed in China. This postponement, among other factors, sparked political activists to speak out against the Chinese government’s neglectful response to the epidemic, an act which may have had them covertly detained.
With the virus being cured at a much higher rate than it is spreading, we can likely put these economic and health concerns behind us soon.