
RATING

Outlook
Negative
SECTOR
Petroleum and Petroleum Products Merchant Wholesalers
Chief Sustainability Officer
T: N/A
E-mail: N/A
Stock Exchange and Ticker
Saudi Stock Exchange (Tadawul): ARAMCO:AB
Website
Contact
T: N/A
E.mail: international.media@aramco.com
Listing
N/A
Awards
- Sabic (Aramco has 70% stake) awarded by Frost & Sullivan for Sustainability and a Circular Economy in the Plastic Recycling Market with Its TRUCIRCLE™ Portfolio
Revenue
$358B
Market Capitalisation
$2.12T
Employees
68,493
Content source
Aramco Sustainability Report
Evaluation of Aramco
Saudi Aramco is committed to meet the higher oil and gas demands and in parallel is taking initiatives to address the negative effects on the environment and community. A close reading of Aramco’s Sustainability Report reveals shortcomings: Only a few specific numerical targets have been identified and progress towards meeting the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) is limited and not convincing as even those that are reported are only based on internal data and not independently verified.
The lack of information can be explained by this being Aramco’s first sustainability report. However, they are reportedly still gathering and analyzing additional KPIs and measuring tools. There are some additional initiatives identified towards 15 of the 17 SDGs (see the Table: UN SDGs Compliance Analysis), but targets and progress only cover five of 17 the SDGs (Table 1: Targets vs Progress Reported).
Aramco seems to be aligning its targets with several industry standards (see Listings, Standards and Frameworks), but information on sustainability awards and industry certificates is limited and not found in sources other than the company’s sustainability report and website.
Furthermore, no third party audits are mentioned in the report to consolidate the reliability of the data presented, which in addition to the lack of certificates, shows either the company’s inability to properly disclose the information or the intention to only disclose the minimum required.
It is a matter of concern that no external audits have been conducted.
Another matter of concern highlighted in the analysis is that Aramco appears to rather invest in offsetting emissions, then in a faster transition towards renewable sources of energy. Projects intended to contribute to sustainable development (e.g. the capture of CO2 in one of their plants in Hawiyah, to pump more oil, as well as similar projects as the Qurayyah Seawater Injection Plant) that were developed several years ago are included in the current sustainability report with no plans of expanding the concepts to other locations.
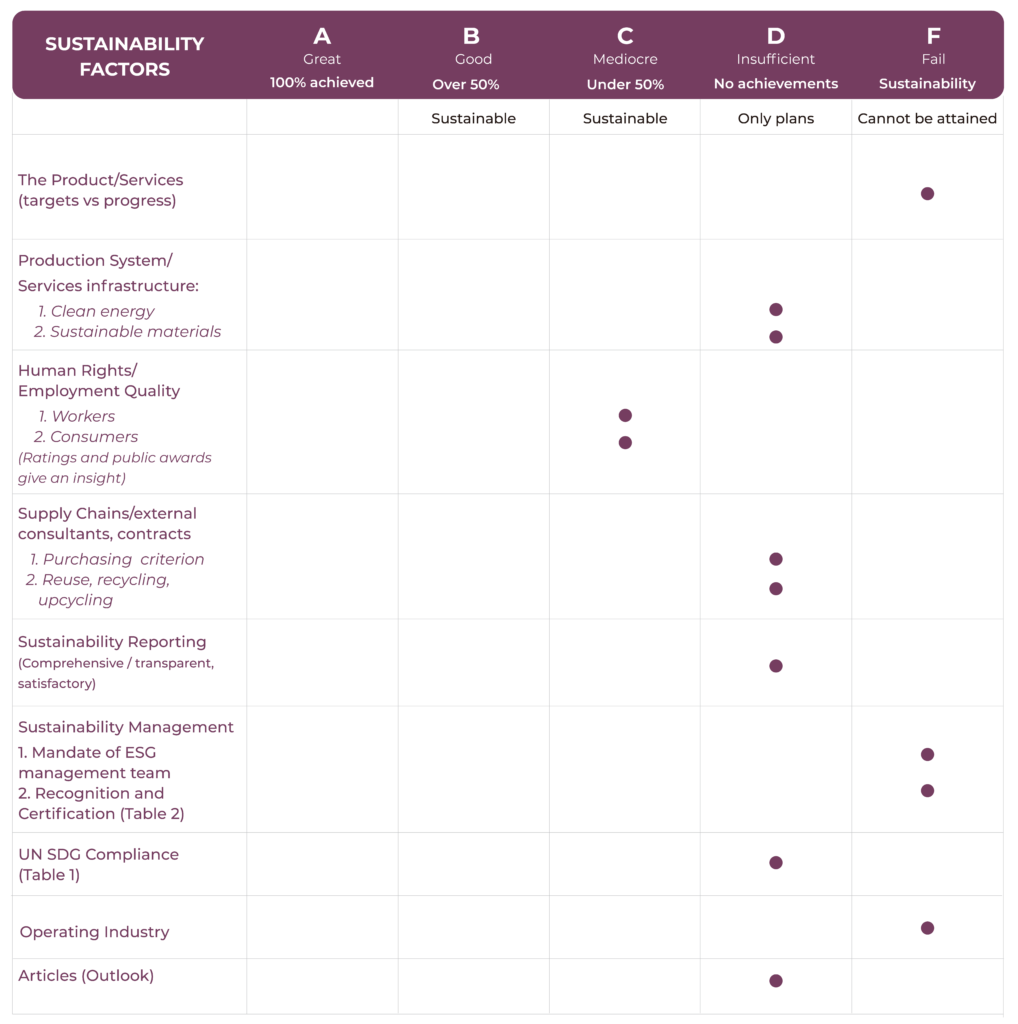
Sustainability Scorecard
Aramco Company Activity
Saudi Aramco, officially Saudi Arabian Oil Company, is a Saudi Arabian state-owned company, engaged in the exploration, production, transportation, and sale of crude oil and natural gas. As of 2021, it is the third-largest company in the world by revenue.
As of December 31, 2021 its reserves included 253.6 billion barrels of oil, 25.2 billion barrels of NGLs; and 194.5 trillion standard cubic feet of natural gas, as well as 530 reservoirs within 137 fields distributed throughout the Kingdom and its territorial waters.
The Downstream segment focuses on refining, logistics, power generation, and the marketing of crude oil, petroleum and petrochemical products, and related services to international and domestic customers. It also supplies oil products; and trades in refined petroleum and liquid chemical products, and polymers.
In addition, the company develops, manufactures, and markets high-performance rubber; and provides crude oil storage, investment, consulting, oil field, insurance, marketing and sales support, financing, and marine management and transportation services.
The company was founded on May 29, 1933 and is headquartered in Dhahran, Saudi Arabia. It has subsidiary locations in Saudi Arabia, China, Japan, India, the Netherlands, the Republic of Korea, Singapore, the United Arab Emirates, Egypt, the United Kingdom, and the United States.
Aramco Sustainability Activity - As per company declarations
The sustainability report starts with positioning Saudi Aramco in the future where “even with the most aggressive climate models, demand for hydrocarbons, though declining, will continue to play an important role in the energy mix for many years to come.” Furthermore, Saudi Aramco states that in many growing markets there will be a need for hydrocarbons well beyond 2050 and therefore the company’s vision is to be “the world’s pre-eminent integrated energy and chemicals company, operating in a safe, sustainable and reliable manner.
In order to meet the world’s energy needs, the company plans to grow the business, by increasing production and delivering energy and petrochemical materials to support economic and social growth, while leveraging technology and innovation to lower emissions and reduce our climate impact.
Aramco recognizes the need to maintain its position as a leader in upstream carbon intensity with one of the lowest carbon footprints per unit of hydrocarbons produced and ultimately decarbonize their own operations by 2050. This is an important part of the focus on long-term shareholder value creation.
Commitment to this goal was reinforced in October 2021, with the announcement of achieving net-zero Scope 1 and Scope 2 greenhouse gas emissions across wholly-owned operated assets by 2050. This complements the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia’s policies in 2021 when it declared its aim to reach net-zero emissions by 2060,as part of the Saudi Green Initiative (SGI). (Source: Saudi Aramco Sustainability Report 2021)
The focus on meeting the world’s energy needs by increasing production, shows that Saudi Aramco has no immediate plans to transition to invest in renewable sources of energy, nor in green chemistry technologies that will eventually eliminate the use of fossil fuel. It seems the company developed its sustainability goals around its main activities of exploration, production, transportation, and sale of crude oil and natural gas.
The company’s newly published sustainability report (June 2021) highlights four focus areas, and targets and progress have been summarized below, through the lens of Sustainable Development Goals.
- climate change and the energy transition;
- safe operations and people development;
- minimizing environmental impact;
- growing societal value
Certificate & Labels, Standards and Frameworks
- ISO 14001
Aramco in the news: Press Reviews and Social Media
Aramco reportedly expects to increase oil production by 1 million barrels a day by 2027 and boost gas production by 50% by the end of this decade.
Aramco began disclosing its emissions in 2019, but Bloomberg noted that those disclosures do not follow practices used by most international oil companies, leaving out vast amounts of emissions that ought to be on Aramco’s carbon ledger. The world’s most valuable company by market capitalization only discloses Scope 1 and 2 emissions. In 2021, those disclosures totaled 68 million metric tons and are expected to reach 67 million tons in 2035. Aramco’s net zero by 2050 target announced last year is also limited to only Scope 1 and 2 emissions.
As Aramco increases oil and gas production, the company’s emissions will inevitably rise. Despite that, Aramco expects emissions in 2035 to remain at 2021 levels through measures such as building plants that capture and bury carbon emissions. Currently, the company has facilities that can store away 800,000 tons of CO₂ and expects to have the capacity to bury 11 million tons by 2035.
This project is described as having the goals of combat desertification, carbon sequestration and biodiversity restoration through the plantation of 26 species of native trees, adaptive to the challenges of the Kingdom environment. The initiative is intended to yield more than 20 million kilograms of carbon sequestration per year while also increasing shade and evapotranspiration, making the local areas cooler.
To consider water scarcity in the area, Aramco has announced it will use water-saving technologies, based on polymers.
The Mangrove Eco-Park opened on January 11, 2021 is the first facility in the Kingdom dedicated to the preservation of mangrove forests. According to Amin Nasser, Aramco’s President and CEO “Mangroves play an important role in the environment as a line of protection and as a nursery for marine life.”
The project started in 2012 and the 63 square km of the Mangrove Eco-Park have been designed, on one hand to educate the community about mangroves, specifically the environmental and economic benefits and secondly, for Aramco to show their commitment to sustainability and to environmental protection.
Between 1992 and 2017 Saudi Aramco had released 5% of industrial carbon dioxide and methane (40B tones of greenhouse gasses). The company has launched a rebranding campaign in an effort to position the company as an environmental leader. Furthermore, the CEO of Aramceo, Amin Nasser helped found the Oil and Gas Climate Initiative to show the oil industry’s pledge to achieve global zero emissions.
Conversely, Aramco companies together with US oil giants shape the energy debate largely through industrial trade groups such as American Fuel & Petrochemical Manufacturers (AFPM). Motiva Enterprises, through which Saudi Aramco owns several refineries and chemical plants in US, is a member of the AFPM, whose actions defeated Washington State ballot Initiative 1631, a state referendum designed to institute a carbon tax. Additional funds from AFPM were given to Heartland Institute to declare that there is no human cause or evidence for climate change.
Lastly, money from AFPM has been distributed to other groups (American Legislative Exchange Council, the Competitive Enterprise Institute, and the American Energy Alliance) that have lobbied against renewable energy policies.
Aramco is a major board member to the American Petroleum Institute, a powerful lobbying group with influence in Washington DC.
Notably, Aramco hired in 2019, through its Motive subsidiaries a lobbying firm (Nickles Group) to influence regulatory policy. Despite all the lobbying, the company’s fears about a shift away from oil was reflected in 2019 in its first-ever bond sale used to fund the acquisition of the Saudi Arabian plastics and chemical firm, Sabic. The company announced in March 2019 that with the acquisition of Sabic, Aramco is planning to utilize non-carbon-intensive products for its petroleum wealth.
Highlights from Aramco Sustainability Report
Achievements
- In 2021, Scope 1 emissions increased by 4% following the start up of the Fadhili Gas plant.
- In 2021 decrease of 14% in Scope 2 emissions due to a shift in consumption of electricity from third-party to company-owned power generation.In 2021, Aramco, via its subsidiary, Saudi Aramco Power Company joined a consortium led by ACWA Power to develop the 1.5 GW Sudair solar plant or 70% of the renewable energy in Saudi Arabia. The first phase of the project is expected to begin producing electricity during the second half of 2022.In January 2021, Mangrove Eco-Park opened, the first facility in Saudi Arabia dedicated to the preservation of old growth mangrove forests. The 63 km2 Mangrove Eco-Park protects one of the last naturally occurring mangrove forests in the Eastern Province of Saudi Arabia and features the longest mangrove boardwalk in the country
- Saudi Aramco has now two projects completed to provide de-salinized water to their plants (Qurayyah Seawater Injection Plant and Khurais Increment Project), yet there is a slight increase in freshwater consumption in 2021 by 1 million cubic meters, indicating that the goal of using de-salinized water has not been attained
- In 2021, sustainability-related R&D was $315M, (52% of total 2021 R&D)
- Altamayyuz Academy, founded in 2021, is an initiative of Aramco to partner with the world’s leading investment banks, accounting firms and the Technical & Vocational Training Corporation (TVTC) to create an academy to educate the Kingdom’s future finance leaders;
- In 2021 the Namaat Program’s industrial investment added 22 new MOUs and one joint venture, focusing on building capacity in four key sectors: sustainability, technology, industrial & energy services, and advanced materials;
- In 2021, the iktva program achieved 59% local content in Aramco’s supply chain, an increase of 35% since 2015
- To date, iktva has contributed an estimated $100 billion to Saudi Arabia’s economy;
- In 2021, the number of serious accidents in blackspots decreased by 68% as a result of Traffic Safety Signature Programs, which provided engineering and enforcement recommendations;
- In 2021,the US-based refinery business Motiva’s Terminals & Pipelines was recognized, seventh time, by the International Liquid Terminals Association (ILTA) with the organization’s 2021 Safety Excellence Award.
Weaknesses and Setbacks
- Aramco relates biodiversity and human rights with the material issue, with various KPIs that need to be measured and the company claims in their sustainability report that in order to ensure the quality and integrity of the data captured, they are applying rather a phased approach and therefore no publicly reported KPIs are available for 2021;
- Aramco does not provide info on Scope 3 emissions, generated when customers burn the oil and gas extracted by the company and are likely to exceed 1.6 billion tons, according to a Bloomberg Opinion estimate. If correct, that amounts to more than 3% of global annual greenhouse gas emissions;
- Furthermore, the company also leaves out emissions from assets in which it shares ownership which means that emissions from many chemicals and refining plants — some of them among the world’s largest — are not counted and those could add up to tens of millions of metric tons of CO₂-equivalent in Scope 1 and 2 emissions, according to Bloomberg calculations.
Targets vs Progress Reported
| Target | Results reported |
|---|---|
| Reduce upstream carbon intensity by at least 15% by 2035 | Carbon capture, utilization and storage (CCUS) - Key assets and storage capacity identified: Wasit, Fadhili & Khursaniyah; - Joint feasibility studies conducted; - Memorandum of Understanding (MOUs) in place with international partners; - As of 2021, achieved an average thermal efficiency of 70.8% due to conversion of energy released from the combustion of fuel into power and steam. |
| Develop CCUS capacity to capture up to 11 MMt CO2e by 2035 | - The CO2 EOR Demonstration Project has a capture capacity of 800,000 tons of CO2 per year; - The captured CO2 (in the plants in Hawiyah) is piped 85 kilometers and pumped into a mature area of an oil field (Uthmaniyah oil reservoir) to enhance oil recovery (EOR) and sequester CO2; - Since the initial injection of CO2 in 2015, the company has doubled oil production rates which implies a more efficient extraction system. |
| Reduce the net Scope 1 and Scope GHG emissions from both the Upstream and Downstream businesses by 52 MMt CO2 by 2035 | - 308 energy initiatives implemented; - Supplying 11.85 mboed energy savings; Equivalent to 1.26 MMtCO2 reduction; - 2021 30% share in 1.5 GW Sudair solar PV project; - Investment in 12 GW of solar PV and wind projects; - 2022 evaluation of share in 2.3 GW of new projects; - In 2021, 300 energy initiatives implemented in, in-Kingdom facilities, resulting in 11.85 mboed of energy savings, (=1.26M tons of CO2 emission reduction) |
| Near zero upstream methane intensity by 2030 (OGCI commitment) | - Current upstream methane intensity of 0.05% |
| Zero Routine Flaring by 2030 (commitment to World Bank) | - Maintained a flare volume of < 1% of total raw gas production since 2012 |
| Target production of up to 11 million tons per annum (MMTPA) of blue ammonia by 2030 | - In 2021, Aramco signed a MOU with Japan’s largest refiner, ENEOS, to consider development of a CO2 -free hydrogen and ammonia supply chain through a year-long feasibility study; - The CO2 captured during the process of converting of hydrocarbons to hydrogen and then to ammonia, was used in methanol production at SABIC’s Ibn-Sina facility, as well as in the Enhanced Oil Recovery demonstration project - this shows feasibility even though results are still scarce |
| Net positive impact on biodiversity through mitigation and compensation | - In March 2021 was approved the company’s first Biodiversity Protection Policy; - Aramco’s priorities for species conservation include top 20 species that have received the highest score from being endangered, few individual left and if it’s unique both globally and within the Kingdom; - As of 2021, 977 km2 of Aramco land has been designated a protected area, comprising 10 Biodiversity Protection Areas, marking a start; - 30% of all of Saudi Arabia’s terrestrial mammal species have been recorded within the company’s Abha protected area |
| Plant 300 MM mangroves by 2035 in KSA and 350 outside KSA | - In 2021 alone, they planted 7 million mangrove seedlings |
| Help farmers produce 800 tons annually of renowned Khawlani coffee beans by 2022 | - Expanded coffee production to Jazan, Aseer, Al-Fifa, Al-Eydabi, Al-Ardhah, Al-Raith, Haroob; - 1000 local coffee farmers; - 200,000 seedlings and the use of a smart & modern irrigation system |
| 150 tons of honey annually by 2022 | - Currently produce 120 tons of honey; - Al-Bahah, one of the region’s cities, is home to more than 3,000 beekeepers |
| Zero target fatalities | - One fatality recorded in 2021 consisted in a death and a full investigation started to identify root causes, spread the lessons throughout our organization and developed action plans to avoid recurrence of such incidents; - 11 Tier 1 process safety incidents occurred during 2021 compared to 9 in 2020, none resulted in operational interruption or loss of life and most of them were minor in nature with 3 resulting in injuries |
| Zero tolerance for unethical behavior | - In 2021, 539 allegations (2020: 619) were recorded, 33 of these cases were investigated for breach of the Aramco Code of Conduct. Allegations had spiked; - The overall trend points to a consistent increase (versus 2019: 507) in the allegations received through the hotline, partly driven by management’s message of zero tolerance for unethical behavior and insistence for all to report on incidents, Aramco states |
| Double the number of female employees in-Kingdom and with 10% of in-Kingdom leadership positions to be held by women, by 2030 | - 5.6% women employed (4.9% in 2019 as the base year); - 3.1% women in leadership positions (2.1% in 2019 as the base year) |
UN SDGs Compliance Analysis
Progress made toward SDG targets
As reported by Aramco

- An employee-wide well-being engagement survey conducted in 2020 found strong employee engagement at 85% with a 95% participation. The results of the survey contributed to the launch of the “Emotional Health and Well-Being Program” across the entire company
- Aramco’s Code of Business Conduct includes specific principles regulating Anti-Bribery and Corruption
- Zero tolerance for unethical behavior

- 50% female students participation in the Summer Enrichment & Tomooh programs;
- 44% female students participation in Internship Programs
- 48% female students participation in College Preparatory Program (CPP)
- Aramco also run a variety of programs to attract and nurture young Saudi talent
- The Young Leaders Advisory Board (YLAB) program serves as a bridge between the youth of Aramco and executive management

- In 2021, Aramco developed and endorsed a Corporate Waste Management initiative
- Aramco is monitoring and reporting waste KPIs through online analyzers
- In 2021, a total volume of 14,447 bbl of oil spills
- In 2021, the Aramco’s consumed 33.8 million cubic meters compared to 32.9 in 2020, an increase due to inclusion of water use by well completion activities in upstream operations. There are no specific targets, nor initiatives to reduce fresh water consumption

- Saudi Aramco plans to invest in 12 GW of solar PV and wind projects

- Road safety initiatives for the workforce, but also to help communities:
- over 200,000 students have received training through “Traffic Safety Gardens”;
- Traffic Safety Kit introduced to train 6,000 teachers (train the trainer) and 1.8 millions students have been trained.
- Established own female driving school;
- Traffic safety awareness programs that included 230 sessions targeting more than 2400 individuals;
- The “Learning from Incidents Series” launched in 2021 is structured to highlight incident failure mechanisms, timelines, causal factors, root causes and major recommendations to prevent reoccurrence and to disseminates the learnings across all business lines and operations;
- Safety Management System (SMS) in place and provides a framework to help the company fulfill the safety and loss prevention expectations. The SMS was evaluated by an independent third-party which found to be comprehensive, mature, and composed of a broad based set of expectations governing how safety is managed;
- In 2021 surveys conducted by Aramco’s insurance broker rated the surveyed facilities as ‘Above Standard’ in terms of spacing and layout; facility inspections; preventive maintenance programs; and Safety Management System implementation, monitoring, and performance KPIs;
- 52 corporate safety assessments or Loss Prevention Compliance Reviews (LPCR) were carried out in 2021 by in-house subject matter experts to independently assess the SMS and compliance programs. In depth analysis are performed on the data gathered and presented to the Aramco’s HSSE Committee for review and further improvement of safety performance;
- Global Company Safety Policy addresses emergency preparedness and is put into action by the corporate SMS via corporate requirements documentation;
- In 2021 the Contractor Camp Environmental Health Inspection Program, a world-class well-being program for the Aramco contractor workforce, has been enhanced to include four key elements:
- 24/7 Hotline and counseling;
- Well-being assessments;
- An online platform with educational content;
- A well-being awareness program.
- In order to monitor safety observations, near misses and incidents for both employees and contractors, Aramco developed SafeLine, fully mobile-compliant on both iOS and Android devices, enabling real-time access to work sites;
- Part of Aramco’s digital transformation in safety, a number of high-impact and proven technologies were adopted to drive safety performance:
- Auto Well Space Out initiative, a smart well solution developed to eliminate human error in well control situations, providing additional protection to rig employees, nearby communities, and to the wider environment;
- Well Tubular Safety Program applies machine learning and predictive solutions that prevent tubular failures and hydrocarbon emissions to the surface or underground aquifers;
- Portable, Exposure-free Multiphase Flow Meter (MPFM) are being implemented across the company to minimize personnel interaction with crude production and to reduce exposure to potentially toxic material;
- Aramco respects internationally recognized human rights standards everywhere they operate, in particular:
- the Universal Declaration of Human Rights;
- the Fundamental Conventions of the International Labor Organization;
- the UN Guiding Principles on Business and Human Rights;
- the human rights and labor principles of the UN Global Compact.
- The company’s Code of Business Conduct sets out the rules for responsible behavior and ethical conduct:
- Employees are free to voice their concerns free from any forms of retaliation;
- The company expects and supports their suppliers to advance their human rights efforts, as well as their respective supply chains.

- In 2020 Aramco acquired a 70% stake in SABIC with the goal of increasing conversion of crude oil directly to chemicals and optimize or eliminate several energy-intensive industrial processes;
- The CO2 is recycled at Aramco by chemically transforming it into new products, specifically, Converge®, Aramco’s polypropylene carbonate polyols product line;
- Saudi Aramco Energy Ventures (SAEV) invests in companies developing innovative technologies, to accelerate their development but also ensure deployment in Aramco’s operations:
- Nexwafe (energy efficient and low-cost wastewater aeration);
- InflowControl (specializing in downhole control valves eliminating unwanted water production in oil wells, significantly reducing upstream energy requirements);
- Utility Global Inc (specializing in hydrogen generation reactors, fuel cells and electrolyzers).
- Aramco’s namaat program was launched in November 2020 to strengthen the procurement and supply chain ecosystem of the company by partnering and attracting world-leading companies in various sectors: sustainability, industrials, technology and advanced materials;
- In-Kingdom total value add (iktva) was launched in 2015 and is Aramco’s flagship program to localize the supply chain. Foreign investors that are looking to secure contracts with Saudi Aramco are evaluated and given a score based in the amount of local content in good and services, salaries paid to Saudi nationals, training and development of Saudis, supplier development spending, R&D and company’s revenue (spend from Saudi Aramco only);
- Aramco is investing in a 50 km2 development for energy-related facilities, King Salman Energy Park (SPARK). The city is expected to add $6 billion to the Gross Domestic Product (GDP) and create thousands of jobs.

- Launched the D&I Strategy 2021 Roadshow to accelerate the implementation of the D&I operating model across the company
- Signed the G20 Alliance pledge as an advocate, to enable a D&I external playbook to be published and to share the best practice of Saudi Aramco

- Aramco’s Stakeholder Protection Policy regulates interactions with local communities;
- Environmental Health Code and Environmental Management System is aligned with ISO 14001, and the policies related to land acquisition include principles dedicated to community issues such as environmental impact assessment, handling of land claims, and access to clean water;
- In different countries with different procedures and routines for involving local community stakeholders, Aramco works to comply with national requirements.
- Anyone affected by Aramco’s business activities has access to Aramco’s General Auditor Hotline where they can report any complaint about operations, without discrimination or fear of repercussion;
- In 2021, community investments of over USD 360 million in Saudi Arabia and abroad:
- DOMESTIC
- In 2021, some 14,000 employees donated circa USD 1.6 million with Aramco matching employees’ donations, it resulted in over USD 3.2 million donated to 22 charities benefiting approximately 50,000 people across 17 cities in the Kingdom to mobilize support to underprivileged people;
- In 2021, Aramco re-opened to the public King Abdulaziz Center for World Culture (ithra), a multidimensional cultural destination, to provide workshops, shows and events about how technology affects our lives;
- Recent initiatives to support micro-industries development include:
- a honey industry development project;
- coffee plantation and production;
- initiative in the textiles industry to support women equipping them with sewing skills:
- Located in Dammam, the Qetan Sewing Center trained 47 women and achieved a production capacity of around 82,000 items;
- In Jazan, the Imprint Factory for Clothing & Uniforms supports 50 beneficiaries, both male and female, by training them in the production of military and medical clothing.
- rose oil body care products production in Al Taif involves the training of 40 women, providing them with a sustainable income. In 2021, Aramco launched the Roseyar online store to market and sell the products.
- ABROAD
- Launched recycling awareness campaign among some 20,000 primary school students and local community members from Huli District, Xiamen;
- Aramco Korea signed an agreement with Seoul Metropolitan Government and the MIDAM Scholarship Foundation (MIDAM) to support the “Seoul Learn X Aramco Coding School,” a computer programming course that teaches coding to underprivileged elementary and middle school students in Seoul;
- Aramco donated over USD 150,000 to the ENTHUSE Charitable Trust, a charitable trust which supports STEM Learning, to continue funding the continuing professional development (CPD) of science teachers and other educators of science in UK;
- Aramco supports the City of Houston’s comprehensive “Resilient Houston” plan to mitigate flooding risks and improve climate readiness by planting, distributing, and reforesting 70,000 trees;
- Lead sponsor of the 2021 Marsh Mania event, a marsh planting effort to plant 40,000 stalks of marsh grass along the Texas Gulf Coast region;
Aramco and Motiva donated USD 200,000 to SETERF for Winter Storm Uri Recovery.

- Circular Carbon Economy Program:
- REDUCE through energy efficiency and flaring minimization, fossil fuel reduction through substitution with lower carbon energy sources like renewables, hydropower, nuclear and bioenergy;
- Reuse – CO₂ can be reused in fuels, bioenergy, chemicals, building materials, food and beverages;
- Recycle – CO₂ is chemically transformed into new products such as fertilizer or cement, or synthetic fuels;
- Remove – capture and storage CO₂, while investing in biodiversity projects
- USD 800 million yo be invested in the next two years in Vapor Recovery Units and Vapor Handling Facilities;
- Circular Carbon Economy Program:
- 99.9% SO2 recovery efficiency achieved through sulfur recovery units in refining and gas plants, in tail gas treatment facilities (TGTU) at Fadhili Gas Plant and Jazan Refinery;
- Sabic’s TRUCIRCLE™ initiative, drives forward a circular economy for used plastics

- The CO2 curing technology developed for precast concrete materials can store up to 20% of the CO2 in the concrete to cure, while delivering superior mechanical strength and reducing curing time by a third, equal to a carbon footprint reduction by 33%, compared with the footprint of conventional concrete;
- Aramco is actively engaged in supporting the Riyadh Voluntary Exchange Platform’s development (a trading platform for carbon offsets and credits produced in the Middle East and North Africa) and has signed an MOU with Saudi Arabia’s Public Investment Fund (PIF).

- Aramco’s projects to protect marine ecosystems include coral-reef regeneration and mangrove restoration, particularly in the Red Sea and the Arabian Gulf.
- Scientists and experts at Aramco support environmental projects by providing free access to data collected regarding wave height, currents, dissolved oxygen, water temperature, clarity, salinity and the concentration of chlorophyll, the pigment that provides energy for photosynthesis;
- Support the regeneration of endangered coral reefs by building a series of strong and stable artificial reef structures on the sea bed.

- The Company’s commitment to delivering positive impact biodiversity and ecosystem services in its operational areas supports the Saudi Green Initiative and is informed by IPIECA’s guidance and UN SDGs;
- This goal to plant one million native trees throughout the Kingdom was reached in 2021 and 26 types of native trees have been planted and sustained with excess treated sewage water;
- Investments in biodiversity education and awareness include in 2021 educational visitor centers at the Mangrove Eco-Park in Tarut Bay and the Shaybah Wildlife Sanctuary in the Rub’ al-Khali.

- Aramco’s Supplier Code of Conduct establishes zero tolerance for bribery and corruption by suppliers, contractors, and third-party consultants with whom the company conducts business;
- The company provides regular training to many of these third parties in Anti-Bribery and Corruption (ABAC) and requires recurring certification of their compliance with the Supplier Code of Conduct;
- The Supplier Code, third-party training, and the recurring certification all instruct third parties to report any known or suspected misconduct relating to Company business.

- Aramco is a steering member of The Hydrogen Council, that provides guidance on accelerating the deployment of hydrogen solutions globally;
- Partnership with Repsol to build a synthetic fuel plant in Spain for low-carbon synthetic diesel and jet fuel for automobiles and aircrafts. (2,100 tons/year);
- $1 billion-plus climate investment fund to support the development, implementation, and scale up of innovative low-carbon solutions in oil and gas, other industries, and commercial transportation through OGCI Climate Investments;
- In partnership with the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology, Aramco is developing a CO2 curing technology. The technology is being- field-testing in collaboration with a local cement company;
- Partnership with Training Within Industry (TWI) ltd and Abu Dhabi National Oil Company (ADNOC) to establish the Nonmetallic Innovation Center (NIC) in Cambridge, UK a research center focused on innovation and advancing the use of non-metallic industrial applications;
- Aramco has established ties in the industry with organizations that will assist in the sustainability transition: A founding member of the Oil and Gas Climate Initiative (OGCI), Aramco has partnered with the International Energy Agency, the Clean Energy Ministry(CEM), and the Global Methane Alliance;
- International Petroleum Industry Environmental Conservation Association (IPIECA)
- Aramco is partnering with several international organizations (C4IR Ocean and its Ocean Data Platform) to provide access to data collected and help the global scientific community;
- Aramco supports the Coral Reef Conservation Fund through a partnership with National Fish & Wildlife Foundation;
- Partnerships with Business Disability Forum, and committed to the Valuable 500 pledge to promote disability inclusion for businesses leadership;
- Applied research to ensure Saudi Aramco’s activities do not cause negative impacts on biodiversity. include partnerships with King Fahad University of Petroleum and Minerals (KFUPM) and King Abdullah University of Science and Technology (KAUST).
Sustainability Certificates, Awards and Listings



