RATING

Positive and on its way to a substantial improvement.
SECTOR
Automotive
Chief Sustainability Officer
Stock Exchange and Ticker
OTC:AUDVF
Website
Contact
T: +49 841 890
E.mail: zentrale@audi.de
Listing
- N/A
Awards
N/A
Revenue
$51.5 B
Market Capitalisation
$83 B
Employees
85,750
Content source
Audi Sustainability Report
SECTIONS : Sustainability • Targets • Evaluation • Key Points • Overview
Evaluation of Audi
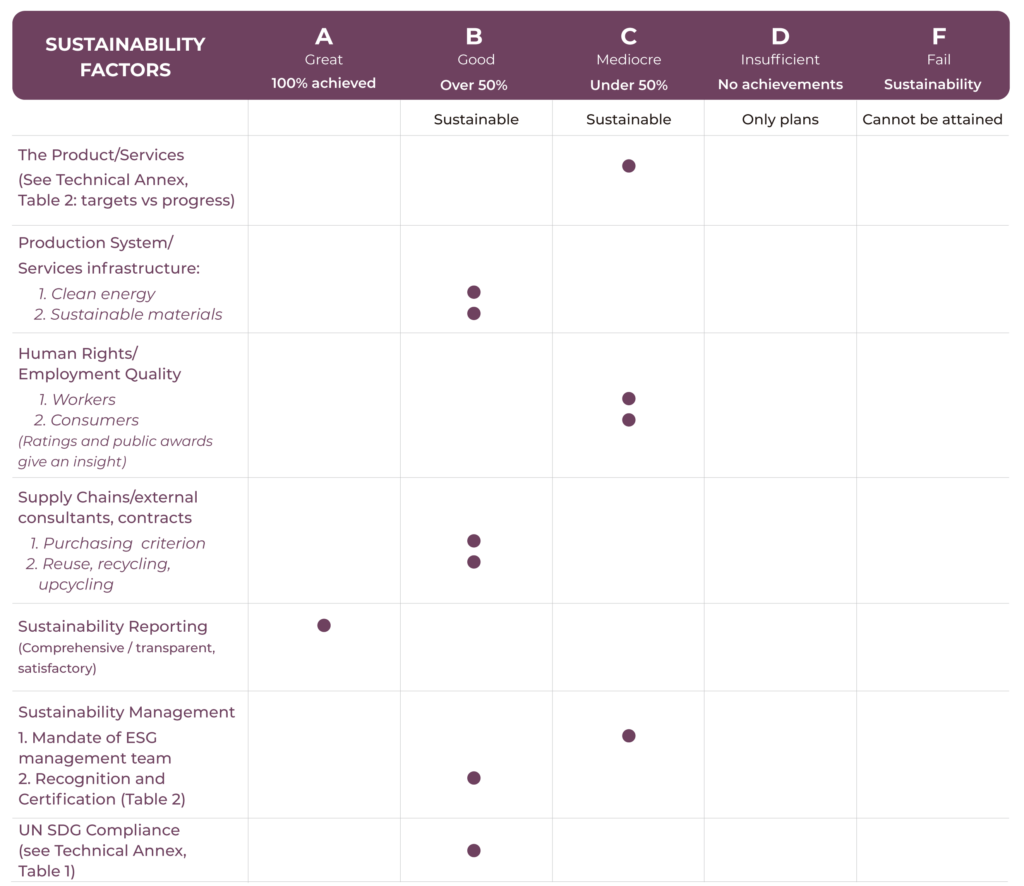
The C score obtained by Audi is explained by several major factors, all contributing to the company not achieving, at least for now, the level of sustainability that it says it aspires to achieve, as summarized in Table 1 of the below.
There is no doubt that Audi is accelerating its changeover to electric mobility: As early as 2026, all new models from the Four Rings on the global market will be fully electric. And in 2033, the Four Rings will shut down the production of vehicles with internal combustion engines. One exception could be China, where the company is investigating the possibility of longer production depending on local demand. Audi has also announced that it already has net carbon-neutral operations for the production of its vehicles at several sites.
Now, according to Audi official documents, the company is focusing more on sustainability throughout the entire product life cycle – from resource extraction and vehicle operation to recycling of the materials used. In the future, ESG (Environmental – Social – Governance) aspects are, according to management, to play an increasingly important role in all the decisions made by Audi, as well as in its products and services. Audi puts forward as its main ESG criteria: climate protection, the use of finite resources, employee health and safety and the perception of social responsibility.
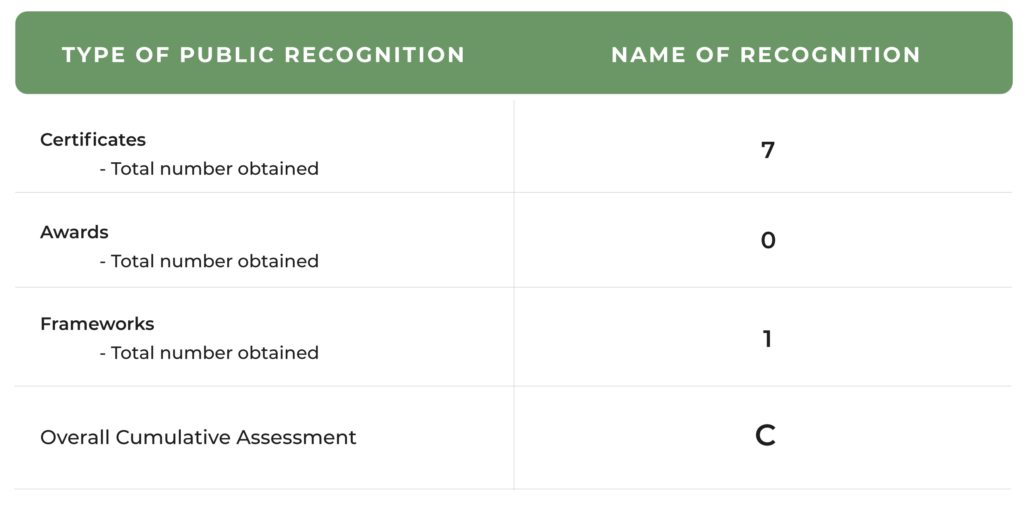
Audi’s sustainability reporting, as shown in the table below, is scored A as it is both transparent and comprehensive; furthermore, it has obtained most of the sustainability certificates that it needs and that are important in the automotive industry (see Table 4 below for details).
Audi’s public image is also positive, and the hiring in 2022 of a well-known climate scientist, Spencer Reeder as its American director of government affairs and sustainability has no doubt helped (more details in the Technical Annex). But on other counts, the results are not so positive. There are setbacks and difficulties (see Table 2), as the progress reported in sustainable production is still generally below 50 percent of the total. One number is emblematic, indicating the length of the road that still needs to be covered: at present, only 10.7% of the total Audi brand production is fully electric and plug-in hybrids.
Company claims to phase out fuel powered cars by 2033 are contradicted by reports that this might not be the case in China where the company is also focusing on the market to sell more cars, one of the largest consumer markets in the world with high potential future consumption growth.
As for the automotive industry in general, the shortage of semiconductors as a result of the COVID-19 pandemic has caused major setbacks for the production of vehicles, making it all the more difficult to achieve sustainability.
Despite the difficulties afore-mentioned, Audi has been able to show a fairly high degree of compliance with SDG targets and its overall score in this regard is “B” (for details, see Technical Annex, Table 3). For example, Audi is an active member of the Global Battery Alliance, which aims to establish a sustainable value chain for batteries, from resource mining through to sustainable recycling. And it has successfully pursued a strategic research partnership for battery recycling. The result: Over 90% of the cobalt and nickel from the high-voltage batteries of the Audi e-tron can be recovered.
Where Audia falls back is in the area of human rights and overall employment quality. For example, it reports that it will increase the proportion of women in the first management tier (i.e. below the Board of Management level) and in the second management tier. As of now, press reports indicate that only 16.8% of managers at the second management level and 8.6% at the first management level are women. This is commendable but still very far from full gender equality.
The company it still is not where it should and can be. Hence Audi is given an overall score of C, close enough to B and with a positive outlook given the company’s avowed determination to achieve sustainability.
Sustainability Scorecard
Audi Company Activity
Audi AG is a German automotive manufacturer of premium cars and motorcycles, headquartered in Ingolstadt, Germany. It is a subsidiary of Volkswagen AG and it has production facilities, together with its subsidiaries in the Americas, Europe, the Middle East and Asia-Pacific.
Audi Sustainability Activity - As per company declarations
Audi is accelerating its changeover to electric mobility: As early as 2026, all new models from the Four Rings on the global market will be fully electric. And in 2033, the Four Rings will shut down the production of vehicles with internal combustion engines. One exception could be China, where the company is investigating the possibility of longer production depending on local demand. Audi already has net carbon-neutral operations for the production of its vehicles at several sites.
Now the company is focusing more on sustainability throughout the entire product life cycle – from resource extraction and vehicle operation to recycling of the materials used. In the future, ESG (Environmental – Social – Governance) aspects are, according to management, to play an increasingly important role in all the decisions made by Audi, as well as in its products and services. Audi puts forward as its main ESG criteria: climate protection, the use of finite resources, employee health and safety and the perception of social responsibility.
Certificate & Labels, Standards and Frameworks
- ISO 14001: Environmental Management and Responsibility
- ISO 50001: Energy Management and Efficiency
- EMAS: management instrument developed by the European Commission for companies and other organisations to evaluate, report, and improve their environmental performance.
- Aluminium Stewardship Initiative (ASI): responsible production, sourcing and stewardship in the global aluminium value chain.
- Performance Standard
- Chain of Custody
- GRI Standard: helps organisations to publicly report the impacts of their activities in a structured way, transparent to stakeholders. Holds the company against NO clear rating system.
- FIA Three-Star Environmental Accreditation
- Gold Certificate of the German Association for Sustainable Building
Audi in the news: Press Reviews and Social Media
Covington, P. (2022) Meet the Climate Scientist Heading Sustainability and Government Affairs at Audi. [online]. Available at:
https://www.triplepundit.com/story/2022/climate-scientist-sustainability-audi/744361
An interview with Spencer Reeder, the director of sustainability and global affairs at Audi America, who is also a climate scientist.
Important to note in the article is Spencer’s feedback, on Audi, but also in general about the importance of aligning government affairs and sustainability goals, pricing carbon in the business systematically, the opportunities and challenges with electric vehicles, charging infrastructure, and batteries lifecycles.
Myles, P. (2022) Audi to End ICE-Powered Vehicle Production by 2033. [online]. Available at: https://www.wardsauto.com/industry-news/audi-end-ice-powered-vehicle-production-2033
The article discusses on one hand Audi’s plan to phase out all global production of vehicles powered by an internal combustion engine by 2033, and its zero environmental program. Phasing out production of ICE-Powered Vehicles includes preparing its global facilities for the production of all-electric cars, as well as building additional capacity, where it is needed.
Secondly Audi is pursuing a zero-environmental program that includes (1) reducing ecological footprint from production and logistics, (2) reduce by 50% “ecologically weighted water consumption value” by 2035, (3) cut by 50% its environmental impact from areas such as energy consumption, power plant emissions, CO2 equivalents, air pollutants, local water risk, and wastewater and waste by 2030.
Investments to address environmental impact will go to generating renewable energy in-house and adopting innovative technologies to create more circular value chains.
Manning, J. (2023) New Battery Passport lets fleets compare the environmental impact of EV batteries. [online]. Available at: https://www.fleeteurope.com/en/new-energies/europe/features/new-battery-passport-lets-fleets-compare-environmental-impact-ev-batteries?a=JMA06&t%5B0%5D=Electrification&t%5B1%5D=Lithium%20ion%20battery&t%5B2%5D=Greenhouse%20Gas%20Accounting&t%5B3%5D=Audi&t%5B4%5D=Tesla&curl=1
Audi and Tesla published their draft of the Battery Passport, initiative launched by the Global Battery Alliance (GBA), a non-for-profit organization driving change across the battery value chain. The passport is designed to provide transparency for investors, end-consumers and other stakeholders related to greenhouse gas emissions from the sourcing and processing of raw materials, and the manufacture of batteries, as well as to any issues of child labour and human rights violations in the mining of the metals and minerals required in the manufacturing of batteries.
Highlights from Audi Sustainability Report
Achievements
- 57.5% increase in share of all-electric vehicles in deliveries compared to the previous year
- 43,866 Audi e-tron models were produced at Audi Brussels in 2021
- 80% of the total of 370 criteria were fulfilled by Audi for initial certification by the Top Employers Institute
- 16.8% of managers at the second management level and 8.6% at the first management level are women
- A net total of more than 195,000 metric tons of CO2 are prevented at the Audi sites in Inglostadt, Neckarsulm, Gyor and the bulti-brand site in Bratislava thanks to a closed-loop aluminum process that AUdi has been using since 2017
- Around 150 countries are currently included in the global pilot project in which Audi is using Artificial Intelligence (AI) to analyze the extent to which suppliers meet the defined sustainability criteria
- A net total of more than 195,000 metric tons of CO2 are prevented at the Audi sites in Inglostadt, Neckarsulm, Gyor and the bulti-brand site in Bratislava thanks to a closed-loop aluminum process that AUdi has been using since 2017
Weaknesses and Setbacks
- Claims to phase out fuel powered cars by 2033, but reports that this might not be the case in China where the company is also focusing on the market to sell more cars, one of the largest consumer markets in the world with high potential future consumption growth.
- As for the automotive industry in general, the shortage of semiconductors as a result of the COVID-19 pandemic has caused major setbacks for the production of vehicles.
Targets vs Progress Reported
| Target | Results reported |
|---|---|
| Carbon neutral production at all its sites by 2025 | Almost halved CO2 Scope 1 & 2 emissions from 2019 to 2021 |
| 30% reduction in our carbon footprint by 2025, compared to 2019 | Total CO2 emitted in 2019 amounted to 451,725, in 2021 this figure was 233,062, a 48% decrease in carbon emissions |
| - 30% of the U.S. model lineup is planned to be full battery electric or plug-in hybrid by 2025. - Reduce CO2 emissions from the Audi EU new car fleet by 27% (base year 2012) |
- 57.5% increase in share of all-electric vehicles in deliveries compared to the previous year (4.9% in total in 2021) - 10.7% of fully electric and plug-in hybrids as a proportion of total production of the Audi brand |
| To have more than 20 fully EV models on the market by 2026 by investing more than 18 billion euros for this by 2026 | Q5 e-tron model released in 2021 |
| Phase out combustion vehicles by 2033 | 5% decrease in cars produced from 2020 to 2021 |
| Reduction in production per unit (UEP) of 35% by 2025 | |
| Further gender equality | Increase the proportion of women in the first management tier below the Board of Management to 2% and to 20% in the second management tier |
| Install more than 5,000 additional fast-charging points with charging capacity of up to 350 kW at over 1,000 locations in Europe - using completely renewable energy sources |